
ITALCOM SRL
Registered office: Via A.Bianchi, 8 - 37045 LEGNAGO (VR) – Loc. S. Pietro;
Operational/administrative office: Via Sansovino 4 - 37053 CEREA (VR)
Tel. 0442 621886 Fax 0442 1941400,
email: nikita@italcomsrl.eu
VAT and Tax Code: 03548510233
© 2025 ITALCOM SRL | VAT 03548510233
Privacy policy | Cookie policy

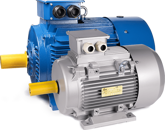
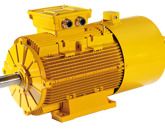
⇨ ENGINES ⇦
Direct Current (DC) Motors:
These motors are widely used for applications that require precise speed control and easy adjustment. DC motors offer good dynamic response and great operational flexibility, but they may require more frequent maintenance due to brush commutation.
Alternating Current (AC) Motors:
AC motors, particularly asynchronous ones, are very common in high-speed bottling lines due to their robustness and durability. They offer good efficiency and can handle heavy loads, but speed control is less precise compared to DC motors. They can be paired with variable frequency drives (VFD) to achieve more precise speed control.
Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are used for applications that require precise and controlled movements. They are particularly useful for the exact positioning of bottles during the bottling process. These motors are used in machines that require high precision, such as in dosing systems or bottle positioning operations.
Brushless Motors:
Brushless motors are very efficient, require little maintenance, and offer high performance. Thanks to their brushless design, they reduce friction and heat dissipation, making them ideal for applications requiring long operational life and high performance. They are frequently used in modern bottling machines, especially in high-speed ones.
Synchronous Motors:
Synchronous motors are used when it is necessary to maintain a constant speed regardless of load variations. They can be powered by alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC), and are often used in machines that require precise synchronization of movement, such as in bottle transport systems.
Motors with Variable Frequency Drive (VFD):
AC motors combined with a variable frequency drive (VFD) allow for very precise and continuous speed regulation. This combination is particularly useful in bottling machines that require frequent speed adjustments to accommodate different bottle sizes and shapes.











⇨ REDUCERS ⇦
1. Cylindrical Gear Reducers (Straight or Helical Teeth)
Description: These are among the most common reducers in bottling machines. Cylindrical gears can have straight or helical teeth. These reducers are used to reduce motor speed and increase torque.
Advantages: They are very robust and reliable, ideal for high-speed applications.
Use: Widely used for speed reduction in bottling lines where high efficiency and power transmission are required.
2. Planetary Gear Reducers
Description: Planetary gear reducers consist of a central gear (sun) and multiple gears (planets) that rotate around it. These reducers are very compact and offer high reduction capacity.
Advantages: They offer high torque density, compactness, and durability. They are ideal for applications requiring high reduction in a small space.
Use: Used in bottling machines where space is limited or where a high torque and high efficiency reducer is needed.
3. Worm Gear Reducers
Description: This type of reducer uses a worm (a helical gear) that meshes with a gear wheel. The main feature is the ability to effectively reduce speed.
Advantages: Efficient for reducing motor speed and achieving high torque. They are compact, with a good reduction ratio, and can be used to orient gears in different directions.
Use: Suitable for applications requiring very high reduction and low speed, such as in bottle transport or handling stages.
4. Bevel Gear Reducers
Description: Bevel gear reducers use bevel gears to transmit rotary motion between two shafts that are at an angle to each other, usually 90 degrees.
Advantages: Effective for applications where a specific transmission angle is needed, such as in bottle transport systems.
Use: Used for applications where it is necessary to deviate the rotation axis, such as in some transmission mechanisms in bottling lines.
5. Right Angle Gear Reducers
Description: Right angle gear reducers are similar to bevel gear reducers but are specifically designed to transmit motion at a 90-degree angle. These reducers can have bevel or helical gears.
Advantages: They offer a compact and highly efficient solution for transmitting power in tight spaces.
Use: Used when it is necessary to change the direction of rotation by 90 degrees, typically in conveyors or bottle handling systems.
6. Rack and Pinion Gear Reducers
Description: This type of reducer transforms rotary motion into linear motion using a pinion (circular gear) that works on a rack (linear gear).
Advantages: Excellent for applications requiring precise linear movements.
Use: Used in bottling machines that require controlled linear movements, such as in bottle positioning or loading and unloading operations.
7. Friction Gear Reducers
Description: Friction gear reducers use a clutch system to reduce motor speed and transfer torque.
Advantages: They allow very smooth power transmission and are suitable for situations where dynamic speed variation is necessary.
Use: Used in applications requiring some speed modulation, such as in bottling machines with different bottle formats.
8. Servo Motor Gear Reducers
Description: These reducers are designed to pair with servo motors and provide very precise torque and speed control.
Advantages: They offer high efficiency, high precision, and rapid dynamic response, ideal for high-speed and precision machines.
Use: Used in high-speed bottling machines or applications requiring precise position control.














⇨ BLOWERS ⇦
1. Centrifugal blowers
Description: Centrifugal blowers are among the most common in bottling lines. These blowers use a rotor that accelerates the air and directs it towards the outlet, creating a high-pressure airflow. The design allows for high flow capacities with good energy efficiency.
Advantages: High airflow capacity, energy efficiency, and ability to work at high pressures.
Use: They are mainly used for transporting bottles along the production line, for orienting or cooling the bottles. They are also used for cleaning empty bottles before bottling.
2. Lobe blowers (screw blowers)
Description: Lobe blowers, or "lobe blowers," use two rotating lobes that interact to compress and push the air out. These systems are very efficient for generating low-pressure but high-flow air streams.
Advantages: They offer good operational stability and are very suitable for continuous and low-pressure airflows.
Use: They are used in applications that require a constant and precise airflow, such as moving bottles or cooling them.
3. Piston blowers
Description: Piston blowers are a type of compressor that uses a piston to compress air. These blowers are generally smaller and more compact than other types and can generate very precise airflows.
Advantages: High precision in airflow control, making them ideal for applications requiring more controlled and low-pressure flows.
Use: They are used for specific operations requiring low-pressure and high-precision air, such as cleaning bottles or precisely positioning them on the bottling line.
4. Radial blowers
Description: Radial blowers, similar to centrifugal blowers, push air along a radial path, creating a high-speed and high-pressure flow. Unlike centrifugal blowers, radial blowers can be designed to operate more quietly and with reduced vibrations.
Advantages: Good air transport capacity and less noise compared to centrifugal blowers. Excellent efficiency in confined spaces.
Use: Often used for transporting bottles or containers in automated systems, as well as for cleaning bottles entering bottling lines.
5. Rotary piston blowers
Description: Rotary piston blowers are a variant of traditional piston blowers. In these blowers, the piston rotates, generating high-speed airflows. They are designed to ensure a constant and powerful airflow.
Advantages: Suitable for high airflows at moderate pressures, good operational efficiency.
Use: Often employed for cooling bottles, moving them along the production line, and cleaning them before filling.
6. Axial fan blowers
Description: Axial blowers are designed to generate an airflow directed along the motor's axis. These devices are very efficient for moving large volumes of air at low pressure.
Advantages: Excellent for high-flow, low-pressure airflows, with low energy consumption.
Use: Mainly used for cooling bottles, orienting them, and removing dust or other impurities from bottles or containers before bottling.
7. Screw compressor blowers
Description: Screw compressor blowers operate through a screw mechanism that compresses air in a cylinder. They are ideal for achieving constant and high-pressure airflows with relatively low energy consumption.
Advantages: High efficiency, low noise, and ability to handle continuous and high-pressure airflows.
Use: They are used in high-speed bottle transport phases or in cooling bottles on high-capacity production lines.
8. Reverse flow blowers
Description: Reverse flow blowers are used to create an airflow that can be reversed or dynamically controlled. This is useful for operations requiring quick and controlled cleaning.
Advantages: They allow very precise and flexible airflow control, ideal for cleaning and orienting bottles.
Use: Used for cleaning bottles and for applications where a reversed or flexible airflow is necessary.








.png)
⇨ PUMPS ⇦
1. Piston Pumps
Description: Piston pumps are positive displacement pumps that use a piston moving within a cylinder to displace the fluid. Each stroke of the piston moves a fixed amount of liquid.
Advantages: High precision and ability to handle viscous liquids or those with solid particles. They can also ensure a continuous and constant flow.
Use: They are used for high viscosity liquids (such as oils, concentrated juices, syrups) or in situations requiring precise volume distribution, such as in food and beverage bottling lines.
2. Peristaltic Pumps
Description: Peristaltic pumps work by passing the fluid through a tube that is compressed by a series of rollers. The movement of the rollers creates a peristalsis that pushes the liquid forward.
Advantages: Suitable for sensitive liquids, such as fruit juices or delicate beverages, as they never come into contact with moving parts. They are also ideal for viscous liquids and for transporting fluids with solid particles.
Use: Mainly used to transfer fruit juices, pulp-based beverages, or food products that need to be handled gently.
3. Gear Pumps
Description: Gear pumps are positive displacement pumps that use gears to move the fluid. The fluid is trapped between the gear teeth and transported along the pump body.
Advantages: Suitable for viscous liquids and applications where a constant and stable flow is necessary. They are generally more compact and simpler compared to other types of positive displacement pumps.
Use: Used for oils, syrups, concentrated juices, or other viscous substances where maintaining a regular flow is important.
4. Diaphragm Pumps
Description: Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm that moves back and forth to create a vacuum that sucks in and then pushes the liquid. This type of pump is positive displacement and relies on the alternating movement of the diaphragm.
Advantages: Ideal for high viscosity, chemically reactive liquids, or those containing suspended solids. They are also very reliable and safe, with the ability to operate at high pressures.
Use: Used for viscous liquids, such as paints, syrups, but also for beverages that require a contamination-proof pump.
5. Centrifugal Pumps
Description: Centrifugal pumps are dynamic pumps that use centrifugal force to push the fluid through the pump. The fluid enters the pump through a central inlet and is pushed outward through an impeller.
Advantages: They are very efficient for low viscosity liquids, high flow rates, and low pressure. They are ideal for handling large volumes of liquid continuously.
Use: Commonly used for transporting water, juices, soft drinks, beer, wine, and other low viscosity liquids in bottling lines.
6. Screw Pumps
Description: Screw pumps use a rotating screw to move the liquid along a path. They are positive displacement pumps, so they move a constant amount of liquid with each rotation cycle.
Advantages: Excellent for viscous liquids, as they ensure a smooth and continuous flow without damaging the fluid. They can operate at low speeds and handle high pressures.
Use: Mainly used for viscous liquids, such as oils, sauces, pastes, and concentrated fruit juices. They are also used for high viscosity fluids in food bottling lines.
7. Lobe Pumps
Description: Lobe pumps are another type of positive displacement pump that uses two rotating lobes to move the liquid through the pump. The lobes rotate synchronously, trapping the liquid between them and pushing it towards the outlet.
Advantages: Great for viscous liquids, as they offer a smooth and precise flow. Lobe pumps are also easy to clean, making them suitable for hygienic applications.
Use: Used in food and beverage applications, such as transferring juices, syrups, yogurt, and sauces, where gentle and precise product handling is necessary.
8. Spiral Pumps (or Helical Pumps)
Description: Spiral or helical pumps are similar to screw pumps but use a spiral rotating within a casing to move the fluid. Like screw pumps, they are positive displacement and move a fixed amount of liquid per rotation.
Advantages: Excellent for handling high viscosity fluids and transferring delicate fluids without foaming.
Use: Used for fruit juices, milk, oils, and other delicate food liquids where it is essential to avoid product damage.
9. Cavitation Pumps (Negative Cavitation Pumps)
Description: These pumps are designed to operate under low-pressure conditions where cavitation of the liquid (formation of gas bubbles) can occur. They are particularly useful when it is necessary to move liquids that should not be damaged by air flow.
Advantages: Great for transporting delicate liquids without damaging them.
Use: Mainly used for food and beverage products, especially for liquids that should not be foamed or altered, such as fresh fruit juices or milk.





















⇨ BEARINGS ⇦
1. Ball Bearings
Description: Ball bearings are among the most common and versatile. They combine a circular motion of balls moving between two rings, reducing friction. They can have one, two, or more rows of balls.
Advantages: Low resistance to movement, energy efficiency, easy maintenance, and good wear resistance.
Use: Suitable for low and medium-speed applications, such as in engines, transport wheels, and other moving parts that are not subject to excessive loads. They are often used for light applications in bottling lines.
2. Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Description: Cylindrical roller bearings have rollers (instead of balls) as rotating elements. These bearings are designed to support higher radial loads than ball bearings, thanks to the larger contact area.
Advantages: Greater radial load capacity and longer lifespan compared to ball bearings, particularly suitable for applications with high loads.
Use: Used in bottling lines to support machinery that must handle heavy loads, such as conveyors, handling systems, and filling machines.
3. Tapered Roller Bearings
Description: Tapered roller bearings are designed to handle combined loads, both radial and axial, thanks to the geometry of the tapered rollers. The rollers touch only at one point, reducing friction compared to cylindrical roller bearings.
Advantages: Excellent for handling high and combined loads (radial and axial) and for applications requiring high precision and resistance.
Use: Used to support parts subject to axial and radial forces, such as in bottling machines where movement must be well controlled (e.g., in cap or bottle press parts).
4. Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Description: Angular contact ball bearings are designed to support both radial and axial loads. The arrangement of the balls and the contact angle allows them to withstand axial loads in one direction.
Advantages: Ability to support high axial loads, good performance under high-speed conditions.
Use: Used in applications requiring support for axial forces, such as in bottle orientation systems, press movements, or other applications with significant axial loads.
5. High-Speed Ball Bearings (Precision Ball Bearings)
Description: These bearings are designed to operate at high speeds with high precision, minimizing friction and keeping temperatures low.
Advantages: Optimized to operate at very high speeds and to ensure long life and performance in environments with high rotational speeds.
Use: Employed in bottling lines working with high-speed machinery, such as in labeling, packaging, and bottle handling systems.
6. Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Description: Self-aligning ball bearings are designed to compensate for alignment errors, thanks to having two outer rings shaped like a sphere, allowing the bearing to automatically adapt to small alignment errors.
Advantages: Compensate for alignment errors, increasing durability and reliability. Offer greater tolerance to deformations and misalignments.
Use: Used in bottling machines where slight misalignments of components may occur, such as in conveyors and bottle handling systems.
7. Sealed or Shielded Ball Bearings
Description: These bearings are equipped with seals or shields to protect the balls from dust, contaminants, moisture, and other harmful environmental factors.
Advantages: Protection against dust, moisture, and contaminants, making them ideal for work environments where there is a risk of contamination or exposure to external agents.
Use: Very common in bottling lines, where it is essential to keep the bearing clean to avoid damage and malfunctions, such as in filling machines and bottle conveyors.
8. Spherical Roller Bearings
Description: Spherical roller bearings combine the advantages of ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings. They have two rows of spherical rollers arranged so they can handle both radial and axial loads in both directions.
Advantages: Ability to handle combined loads (radial and axial), suitable for applications requiring high load capacity and wear resistance.
Use: Used for applications with heavy loads and to support moving parts that must withstand both radial and axial forces, such as in some transport systems and industrial machinery.
9. Bearings for Humid or Aggressive Environments
Description: These bearings are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as high humidity, exposure to detergents, solvents, or other chemical fluids.
Advantages: Special materials (e.g., stainless steels or plastic materials) make them resistant to corrosion and degradation caused by fluids and moisture.
Use: Used in bottling lines where machinery is exposed to humid working conditions or environments where there is a risk of corrosion, such as in lines for carbonated drinks, juices, or waters.
10. Magnetic Bearings (Contactless)
Description: Magnetic bearings use magnetic forces to support movement without physical contact between parts. This minimizes friction and wear.
Advantages: No physical friction, long lifespan, and reduced maintenance.
Use: Used in high-precision and high-speed applications, where it is essential to minimize wear and friction, such as in some high-speed bottling machines or sterile environments.
















⇨ ACTUATORS ⇦
1. Pneumatic actuators
Description: Pneumatic actuators are powered by compressed air. They use air pressure to generate linear or rotary motion, depending on the type of actuator.
Advantages: They are fast, easy to control, economical, and ideal for applications requiring quick and frequent movements. They do not require an electrical power supply, so they can be used in environments where electricity is not safe or practical.
Use: Common in bottling lines for transport operations (such as bottle movement), filling, capping, labeling, and automatic selection of bottles or containers.
Main types of pneumatic actuators:
Pneumatic cylinder actuators: Used for linear movement, such as in lifting, pressing, or moving bottle systems.
Pneumatic rotary actuators: Used for rotary movement, such as in bottle closing and capping mechanisms.
2. Electric actuators
Description: Electric actuators are powered by electric motors and convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. They can generate linear or rotary motion depending on the type of actuator.
Advantages: They provide precise control and easy speed adjustment. They can be integrated with advanced control systems, such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), to ensure highly automated and precise operation.
Use: Used in applications requiring precise motion control, such as liquid dosing during filling, precise bottle positioning, and advanced automation.
Main types of electric actuators:
Electric motors with ball screws or lead screws: For precise and high-speed linear movements.
Electric rotary actuators: Used for applications requiring controlled rotations, such as in capping or labeling systems.
3. Hydraulic actuators
Description: Hydraulic actuators use the pressure of a fluid (usually oil) to generate motion. They can generate very high forces with relatively small sizes.
Advantages: Excellent for applications requiring high forces and powerful movements. Hydraulic actuators can be more compact than electric or pneumatic ones for the same load capacity.
Use: Used in applications requiring high force, such as pressing, lifting, or other operations involving heavy loads.
Main types of hydraulic actuators:
Hydraulic cylinders: Used for linear movement applications, such as in compacting, transporting, and material handling stages.
Hydraulic motors: For applications requiring rotary movement, such as in machine drive systems or handling plants.
4. Solenoid actuators (electromagnetic)
Description: Electromagnetic actuators (or solenoids) use a magnetic field generated by an electric current to move an armature within a coil. When the current passes through the coil, the magnetic field attracts or repels the armature, generating motion.
Advantages: They are compact, fast, and ideal for applications requiring quick and precise movements. They are also economical and easy to control.
Use: Used in valve control applications, quick-change systems, closure systems, and automatic selection operations (e.g., to separate empty bottles from full ones).
5. Linear screw drive actuators (ball screws, trapezoidal screws)
Description: These actuators use a screw that, when rotating, moves a mobile part along a linear path. The screw can transform rotary motion into linear motion.
Advantages: They provide precise and high-force movement with good efficiency. They are particularly suitable for applications requiring moderate loads and high levels of precision.
Use: Used in applications requiring slow but very precise linear movements, such as in bottle position control or liquid dosing.
6. Piezoelectric actuators
Description: Piezoelectric actuators work thanks to the ability of certain materials (such as quartz) to deform when subjected to an electric voltage. These actuators are very sensitive and can generate very small but precise movements.
Advantages: Extreme precision in movements, with the ability to generate very rapid movements and small forces. They can be used for high-precision applications, such as component alignment.
Use: Mainly used in high-precision positioning applications, such as in bottle calibration and alignment systems or in managing small liquid dosage quantities.
7. Diaphragm actuators
Description: Diaphragm actuators use a flexible membrane that deforms under the effect of a fluid (air, water, oil) or an electric field, producing linear or rotary motion.
Advantages: They can operate in hygienic or sterilized environments, ideal for applications where contamination or corrosion risks must be avoided.
Use: Employed in bottling applications where contamination protection is required, such as in managing juices, waters, or delicate beverages.
8. Friction actuators
Description: Friction actuators work by applying friction forces between two surfaces, which generate mechanical movement.
Advantages: They can be more compact than other types of actuators and are ideal for applications where movement must be controlled without the use of complex moving parts.
Use: Mainly used for control and selection operations in bottling lines, such as changing the direction of bottles or controlling liquid flow.













⇨ GEARS ⇦
Cylindrical gears: They are the most common in bottling lines, as they allow for simple and linear motion transmission between parallel shafts. These gears are used to efficiently reduce or increase rotational speed.
Bevel gears: Used when it is necessary to transmit motion between shafts that meet at an angle, usually 90°. These gears are ideal for smoothly changing the direction of motion.
Worm gears: Often used for applications requiring a very high reduction ratio. In a bottling line, these gears can be used to reduce motor speed and provide greater torque.
Helical gears: These gears have teeth inclined relative to the axis of rotation and are used to reduce noise and improve efficiency compared to cylindrical gears. They can be used in sections of the bottling line that require high rotational speed.
Planetary gears: These gears consist of a central gear (sun) that interacts with smaller gears (planets) and an outer ring. They are used for applications requiring high-efficiency power transmission and a compact design, such as in high-precision movement parts.
Friction gears: These gears do not always transmit motion continuously. They can be used to control speed or to temporarily stop motion at certain stages of the bottling process.




















⇨ BELTS ⇦
1. V-belts
Description: V-belts (or trapezoidal belts) are one of the most common types. They have a "V" shaped cross-section and fit into pulleys with corresponding grooves.
Usage: They are very common in bottling lines to transmit power between pulleys and to regulate movement speed at different stages of the process. They offer good grip, reduce slippage, and are easy to install and replace.
Variants: They can be made of various materials such as rubber, reinforced polymer, or with special coatings to increase their durability and reliability.
2. Timing belts (or synchronized belts)
Description: Timing belts are designed with a series of teeth that engage with the grooves of the pulleys, allowing for synchronous and precise movement transmission without slippage.
Usage: Used in applications where it is crucial that the movement between the pulley and the belt is perfectly synchronized, such as in dosing systems or capping mechanisms.
Advantages: They offer high precision, slippage-free transmission, and long life, which is why they are frequently used in high-speed bottling lines.
3. Flat belts
Description: Flat belts are made with a rectangular or trapezoidal shape, without grooves. They are made of elastic materials like rubber and are quite wide and thin.
Usage: These belts are used in conveyor belt systems, such as those that move bottles or containers along the bottling line.
Advantages: They have low rolling resistance and can cover greater distances, ideal for transporting light objects or in environments that require low friction.
4. Round belts
Description: Round belts, as the name suggests, have a round cross-section and are typically made of rubber or similar materials.
Usage: They are often used for light transmissions in bottling lines, especially in machinery with small pulleys.
Advantages: Round belts are quieter and more wear-resistant than other types of belts, ideal for applications requiring greater durability and resistance.
5. Polyurethane belts
Description: Polyurethane belts are belts with high wear resistance, made of synthetic material that offers excellent load characteristics and long life.
Usage: These belts are used in high-speed applications or where a high degree of resistance is required, such as in transport sections or in washing or sterilization machines.
Advantages: Excellent resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and weather conditions, making them particularly suitable for harsh working conditions.
6. Low-stretch belts (steel cables)
Description: These belts are made with steel or aramid fiber reinforcements to minimize stretch and maintain precision over time.
Usage: They are used in applications where high strength and constant power transmission are necessary, such as in high-speed sections of bottling lines.
Advantages: They are ideal for high loads and environments where continuous vibrations or stresses occur.
7. Conveyor belts
Description: Conveyor belts are a form of long, continuous belt used for transporting bottles or other containers along the bottling line.
Usage: They are used to move containers from one machine to another, such as from the filling machine to the capping machine.
Advantages: They allow the transport of a large number of bottles or containers continuously and efficiently, reducing the need for interruptions in the production flow.




.png)



⇨ CHAINS - CARPETS - TAPES ⇦
Roller chains (or standard roller chains)
Description: Roller chains are one of the most common types of chains and are composed of a series of rollers mounted on pins. These chains are designed to transfer heavy loads and allow the smooth movement of containers.
Usage: They are used for transporting bottles and other containers along the bottling line, especially when high load capacities are required.
Advantages: High strength, long durability, ability to handle heavy loads, and reliability in tough working conditions.
Flat top chains (or horizontal flat top chains)
Description: Flat top chains are formed by plates or horizontal planes connected by pins and are designed to provide continuous and stable support for containers during transport.
Usage: They are used in applications where stable and secure transport of containers is necessary, especially in filling or capping machines, or where containers need to be positioned precisely.
Advantages: They provide stable and constant support, reducing the risk of tipping or damage to containers.
Wide link chains (or wide pitch chains)
Description: These chains have wider links and a structure that allows the passage of dust or liquids, making them ideal in high humidity production environments or for transporting larger and heavier objects.
Usage: Used in bottling lines that require the transport of large or heavy objects, such as crates or large containers, or when continuous cleaning is crucial.
Advantages: The wide links promote greater ventilation and easy cleaning, reducing dirt accumulation issues.
Double pitch chains
Description: These chains feature two rows of rollers or planes, allowing them to support a greater load and operate more stably.
Usage: They are used when heavy loads need to be handled or when containers need to be transported at high speeds evenly.
Advantages: They are robust and durable, ideal for high-capacity production environments.
Special stainless steel chains
Description: Stainless steel chains are particularly resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them ideal for bottling environments where liquids and chemicals are involved.
Usage: They are used in bottling lines that handle food products, beverages, or other applications where corrosion resistance is crucial.
Advantages: High corrosion resistance, long durability, and ease of cleaning.
Flat surface conveyors (flat belts)
Description: These belts consist of a continuous and flat surface that slides over rollers. They can be made from various materials, including rubber, PVC, or polyurethane.
Usage: Used to transport bottles, cans, or other containers along the bottling line. They can be inclined or flat, depending on specific needs.
Advantages: They offer a smooth and continuous surface, ideal for stable transport of containers.
Modular belts (interchangeable module belts)
Description: Modular belts are made up of small interconnected sections that can be replaced individually, reducing maintenance costs and facilitating cleaning.
Usage: Used in high-speed bottling lines where maintenance and cleaning are frequent. They are perfect for transporting bottles or other containers safely and precisely.
Advantages: Easy to replace and repair, suitable for environments requiring high hygiene and frequent maintenance.
Wire mesh conveyors (or wire mesh belts)
Description: These belts are made of metal meshes, often stainless steel, and are used in high-temperature environments or where high corrosion resistance is required.
Usage: They are employed in bottling lines where robust support for containers or bottles is necessary, especially in hot environments such as sterilization or pasteurization machines.
Advantages: Excellent temperature and corrosion resistance, long durability, easy to clean.
Rubber or PVC conveyors
Description: These belts are made of rubber or PVC, materials that offer wear resistance, good grip, and a surface that reduces the risk of container slippage.
Usage: Used in bottling lines where good traction is necessary to transport bottles or cans, especially for high speeds or to transport lighter objects.
Advantages: Flexible, with good ability to adapt to curves and inclines, wear-resistant, and easy to clean.
Slat conveyors (or slat belts)
Description: Slat belts consist of wide and spaced slats mounted on a support frame. These belts offer great resistance to chemicals and heat.
Usage: They are used for transporting bottles or containers that need to be kept stable during movement. Often employed in capping or filling machines.
Advantages: They provide a stable surface for transport and are resistant to chemicals and high temperatures.
















⇨ CONVEYOR BELTS ⇦
1. Flat Surface Conveyors (Flat Belts)
Description: Flat surface conveyors are made with a smooth and continuous surface. They can be made of materials such as rubber, PVC, or polyurethane.
Usage: They are used for transporting bottles, cans, and small to medium-sized containers along the bottling line. They are ideal for linear movements and environments with low inclines.
Advantages: Easy to maintain, simple in design, and excellent for uniform transport of containers.
2. Modular Belts (or Interchangeable Modules)
Description: These belts are composed of small modular sections that can be easily replaced without having to change the entire belt. The modules are usually made of plastic or stainless steel.
Usage: Used in environments where frequent maintenance or cleaning is required. They are ideal for high hygiene environments, such as in the food or beverage industries.
Advantages: Easy to repair, hygienic, and very durable. They offer a long lifespan and can be customized according to specific needs.
3. Wire Mesh Conveyors (or Stainless Steel Belts)
Description: These belts are made of metal meshes and are constructed from stainless steel, making them particularly resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
Usage: They are used in high-temperature applications (such as in sterilization and pasteurization phases), or in environments where robust and resistant transport is necessary.
Advantages: Resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and corrosion, perfect for harsh industrial environments.
4. Rubber or PVC Conveyors
Description: Rubber or PVC conveyors are commonly used in applications that require good grip and flexibility. They can have a smooth or grooved surface.
Usage: Used to transport bottles or cans in bottling lines where good traction is required. They can also be used to move heavier or slippery products.
Advantages: Good wear resistance, high traction, adaptable to curves or inclines, and easy to clean.
5. Slat Conveyors
Description: These conveyors consist of wide slats, usually made of plastic or steel, mounted on a support frame. They offer continuous support and are ideal for transporting larger containers.
Usage: Used to transport larger and heavier bottles or containers, or in applications that require precise and stable movement, such as in filling, capping, or labeling machines.
Advantages: Provide stable support, are durable and easy to clean. They are ideal for applications where stability is crucial.
6. Inclined Conveyors
Description: These conveyors are designed to transport containers uphill or downhill, thanks to their inclination. They can be made from various materials, including rubber, PVC, or metal.
Usage: Used in bottling lines when it is necessary to transport bottles or cans on an incline, for example, to move from one machine to another or to move products between different heights.
Advantages: Excellent for vertical movement of containers, with the ability to avoid overly wide horizontal spaces and optimize space in the production line.
7. Belt Conveyors (Continuous Surface)
Description: These belts have a continuous and uniform surface, often made of rubber or synthetic materials. They are commonly used for transporting bottles and cans on horizontal lines.
Usage: Used for transporting products along a fixed path, ideal for transporting bottles or cans without compromising their integrity.
Advantages: Smooth transport of containers, durable surfaces, and easy to clean, often used in filling, capping, and packaging stages.
8. Textured Surface Conveyors
Description: These belts feature a textured surface that increases traction, reducing the risk of slipping.
Usage: Often used to transport bottles or cans that might be slippery or for applications where uncontrolled movement of containers is to be avoided.
Advantages: Increase transport safety by minimizing the risk of slips, particularly useful in high-speed environments.
9. Spiral Conveyors (or Spiral Elevators)
Description: These conveyors are designed to lift containers continuously along a spiral or helical path.
Usage: Used when it is necessary to move bottles or cans between different height levels in a compact and uninterrupted flow.
Advantages: Optimize space, allowing products to be moved between different levels, reducing horizontal footprint and improving space efficiency in the line.
10. Antistatic Conveyors
Description: These belts have antistatic properties, preventing the buildup of electrical charges during the transport of containers or bottles.
Usage: Used in environments where dust or electrical charge buildup could compromise product quality or the bottling process, such as in electronic or dust-sensitive environments.
Advantages: Prevent damage from electrostatic discharges, improve safety and product quality.
















⇨ PNEUMATIC ⇦
1. Pneumatic cylinders
Description: Pneumatic cylinders (or actuators) are crucial components that convert compressed air energy into mechanical motion. They are used to move or lift containers or to activate other moving machines.
Types of spare parts:
Double-acting cylinders: Used to move containers in two directions.
Single-acting cylinders: Used for movement in one direction, often used in lighter applications.
Cylinder rod: Part that can wear over time.
Cylinder seals: Crucial for preventing air leaks and ensuring system efficiency.
2. Pneumatic valves
Description: Pneumatic valves control the flow and direction of compressed air within the system. They can be of different types, such as flow control valves, directional valves, and safety valves.
Types of spare parts:
Directional valves (e.g., 5/2 or 3/2): Used to change the direction of air flow in cylinders or other components.
Check valves: To prevent reverse flow of air or liquids.
Pins, springs, and seals: Parts that can wear or get damaged over time, causing leaks or malfunctions.
Pressure exchangers: To control the input and output pressure in various stages of the process.
3. Filters, regulators, and lubricators (FRL units)
Description: FRL units (Filter, Regulator, and Lubricator) are essential to ensure that the compressed air entering the pneumatic system is clean, at the right pressure, and adequately lubricated.
Types of spare parts:
Filter elements: Remove impurities or particles from compressed air.
Pressure regulators: Control and maintain constant air pressure in the system.
Lubricators: Add a small amount of oil to the air to reduce wear on pneumatic components.
Seals: Essential to prevent air leaks.
Drain valves: To discharge accumulated moisture in filter systems.
4. Pneumatic pipes and fittings
Description: Pneumatic pipes and fittings are used to connect various system components and to transport compressed air where needed.
Types of spare parts:
Pipes and tubing: Made of materials like plastic or stainless steel, depending on the need for pressure or chemical resistance.
Fittings and joints: Used to join various components and ensure a tight connection between pipes, valves, and cylinders.
Sealing rings and gaskets: To ensure connections are airtight and leak-free.
5. Pneumatic switches and sensors
Description: Pneumatic sensors monitor the operation of pneumatic systems, such as cylinder position or air pressure.
Types of spare parts:
Position sensors: Used to detect the position of pneumatic cylinders.
Pressure sensors: Monitor air pressure at various points in the system.
Limit switches: Used to detect when a part of the system has reached its final position.
6. Air compensators and accumulators
Description: Air accumulators are used to store compressed air and maintain stable pressure in the system.
Types of spare parts:
Membranes and seals: These can wear out and cause air leaks.
Safety valves: Serve to protect the system from excessive pressures.
Accumulator fittings and pipes: Part of the air distribution system.
7. Pneumatic actuators for specific applications
Description: Pneumatic actuators are used to automate processes such as cap closing, container handling, and positioning.
Types of spare parts:
Linear and rotary cylinders: Used to manipulate or position bottles, cans, and containers.
Speed control valves: Used to regulate the movement speed of cylinders.
Pneumatic brakes: Used to stop machines in a controlled manner, such as in labeling or packaging stages.
8. Pneumatic blowers and fans
Description: Used for cooling or for the bottle blowing process (especially for PET bottles), these devices use compressed air to operate.
Types of spare parts:
Blow nozzles: Can wear out due to the continuous passage of high-pressure air.
Air flow control valves: To regulate air flow in blowing and cleaning processes.
9. Gauges and control instruments
Description: Gauges and control instruments are used to monitor air pressure and flow in the pneumatic system.
Types of spare parts:
Pressure gauges: To monitor air pressure.
Control valves: To regulate air flow or return.
10. Pneumatic control units
Description: Pneumatic control units regulate the behavior of the pneumatic system based on electronic or mechanical signals.
Types of spare parts:
Electronic controllers or PLCs: For automatic management of pneumatic components.
Control panels and buttons: For manual control of pneumatic systems.


















⇨ ELECTRONICS ⇦
1. Electric Motors
Description: Electric motors are used to drive various components, such as conveyors, pumps, presses, and other movement mechanisms.
Types of Spare Parts:
Direct Current (DC) Motors: Used for applications requiring precise speed control.
Alternating Current (AC) Motors: More common for high-power applications and operations that do not require fine speed control.
Motor Brushes: For DC motors, brushes can wear out and require replacement.
Motor Bearings: Motors can wear out in the bearings, causing vibrations or noise.
Motor Starters and Protectors: To prevent damage to motors due to overcurrents or short circuits.
2. Inverters and Motor Drives
Description: Inverters and drives are used to control the speed and movement of electric motors, adapting them to the needs of the production line.
Types of Spare Parts:
Inverters (VFD): They modify the frequency of the alternating current to control the motor speed. Spare parts include power circuits and electronic components.
Power Modules: To safely control and distribute power.
Control Buttons: Used to adjust inverter settings.
3. Sensors
Description: Sensors are used to monitor various parameters such as container position, fill level, temperature, and line speed. They are crucial for the automated operation of the bottling line.
Types of Spare Parts:
Position Sensors (inductive, capacitive, magnetic): To detect the position of containers, valves, or actuators.
Level Sensors: Used in filling stages to monitor and control the liquid level in bottles or cans.
Temperature Sensors: To monitor operating temperatures during pasteurization, cooling, and other critical stages.
Speed Sensors: Used to measure the transport speed of bottles along the line.
Photoelectric Sensors: Used to detect objects and bottles, especially for automatic bottle detection during filling, capping, and labeling.
4. PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
Description: The PLC is the "brain" of the bottling line, as it manages and coordinates all automatic operations. It controls motors, sensors, valves, and machine commands.
Types of Spare Parts:
Input/Output (I/O) Modules: To connect the PLC to sensors, actuators, and other devices.
PLC CPU: The central part that processes data and sends commands to machines.
Power Supplies and Modules: To provide energy to the PLC and its components.
Memory and Communication Modules: To store programs and manage communication between the PLC and other devices.
5. Displays and Control Panels
Description: Displays and control panels allow operators to monitor and interact with the bottling line, set parameters, and view operating data.
Types of Spare Parts:
Touch Screens: Used to display operational information and allow operators to interact with the system.
Switches and Control Buttons: To turn machines on/off and adjust parameters.
Indicator Lights: Used for visual alarm signals or machine operating status.
HMI Units (Human-Machine Interface): Advanced control panels to interface with the PLC and adjust the system.
6. Power Supplies and Distribution Circuits
Description: Electrical power supplies and distribution circuits are used to provide stable current to all electrical and electronic components of the bottling line.
Types of Spare Parts:
Switching Power Supplies: To convert electrical energy into direct or alternating current to power devices.
Transformers: To adapt voltage to levels compatible with equipment.
Switches and Fuses: Protect circuits against overloads or short circuits.
7. Relays and Contacts
Description: Relays and contacts are used to open or close electrical circuits automatically or manually.
Types of Spare Parts:
Control Relays: Used to operate motors or pneumatic valves based on signals from sensors or the PLC.
Switching Contacts: To manage the flow of current in electrical and pneumatic circuits.
8. Printed Circuit Boards (PCB)
Description: Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are used to integrate various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, microchips, and transistors.
Types of Spare Parts:
Motor Control Boards: For controlling motors and their speed.
Sensor Control Boards: For managing data from sensors and sending it to the PLC.
Interface Boards: To ensure communication between various electronic devices of the bottling line.
9. Cables and Connectors
Description: Cables and connectors are used to connect all electrical and electronic components of the line.
Types of Spare Parts:
Power and Signal Cables: Used for transporting current and signals between motors, sensors, and PLC.
Industrial Connectors: To ensure secure and stable connections between various components.
Signal Cables for Sensors and Relays: Essential for precise and interference-free communication.
10. Electronic Safety Systems
Description: Electronic safety systems monitor the safe operation of the line, such as fault detection, anomalies, or hazardous situations.
Types of Spare Parts:
Safety Sensors: To monitor and ensure that operations do not cause harm to operators or equipment.
Emergency Stop Systems: Combine electrical circuits and safety devices to stop operation in case of critical failures.









.png)


⇨ CAPPER HEADS ⇦
1. Compression Capping Head
Description: The compression capping head is used to apply caps that require mechanical compression, such as crown or screw caps. The head applies constant pressure to compress the cap onto the bottle, securely sealing it.
Features:
Suitable for metal caps (e.g., crown caps, screw caps).
The closing force is adjustable based on the type of cap and container.
Mainly used in bottling lines for beverages, juices, beers, and other liquids.
Type of Cap: Crown caps, screw caps, plastic caps.
2. Rotating (or Screw) Capping Head
Description: This type of capping head applies a rotary motion to screw the cap onto the bottle. It is designed for caps that need to be screwed, such as screw caps or threaded crown caps.
Features:
Employs a rotating system to screw the cap onto the bottle.
Can be used for plastic or metal threaded caps.
Very common in bottling lines for wines, oils, vinegars, and beverage bottles in general.
Type of Cap: Screw caps, threaded crown caps.
3. Pressure Capping Head
Description: The pressure capping head applies direct pressure on the cap to force it onto the bottle, without a rotary motion. It is widely used for capsule caps or plastic stopper caps.
Features:
Application of closing force through vertical pressure.
Suitable for compression caps or soft plastic caps.
Used for capping wine bottles, liquor bottles, and other beverages.
Type of Cap: Plastic caps (such as caps for wine or liquor bottles), corks for wines.
4. Cap Capping Head (or "Hood Head")
Description: Cap capping heads are designed to apply caps on bottles with a hood closure, such as those used for wine or certain types of liquors. These caps are similar to crown caps but can also be used for more delicate applications.
Features:
They can be equipped with a system that folds or seals the cap around the neck of the bottle.
They use a compression motion or a combination of rotation and pressure.
Type of Cap: Plastic caps, hood-shaped crown caps.
5. Corkscrew (Screw) Capping Head
Description: This type of head is specifically designed to apply screw caps or spiral caps, mainly used in wine bottles. The rotating head screws the spiral cap with precision.
Features:
Rotating system suitable for applying spiral caps.
Commonly used for cork or plastic caps.
Predominantly used in the wine industry.
Type of Cap: Cork caps, plastic spiral caps.
6. Crown Cap Capping Head
Description: Crown cap capping heads are designed to seal bottles with metal crown caps. This type of head is generally used for beer bottles and other carbonated beverages.
Features:
Uses a roller head or hood that folds the cap around the neck of the bottle.
The cap is secured with uniform compression to prevent leaks.
Type of Cap: Crown caps (typical for beer, carbonated drinks, etc.).
7. Roll-On Capping Head
Description: This type of head is used for Roll-On Pilfer Proof (ROPP) caps, which are metal caps with a thread that must be rotated and "crushed" onto the neck of the bottle to ensure an airtight seal.
Features:
The cap is applied with a rotary motion and a high-precision compressor.
The cap is used for wine bottles, spirits, and sometimes for oils and juices.
The head has a "folding" system that seals the cap around the neck of the bottle.
Type of Cap: Roll-On Pilfer Proof (ROPP) caps.
8. Snap-On Capping Head
Description: Snap-On capping heads are designed for caps that easily fit onto the neck of the bottle through a "snap" system. These caps do not require rotation or compression and are more common for plastic containers or bottles with snap caps.
Features:
They are easily applied without rotary motion.
Used for plastic caps or similar materials that "snap" onto the neck of the bottle.
Type of Cap: Snap-on plastic or metal caps.
9. Cork Capping Head (Traditional Corking)
Description: Cork capping heads are specifically designed for sealing bottles with corks, particularly in the wine sector.
Features:
They use a compressive head that applies homogeneous pressure to ensure a perfect seal.
They can be equipped with a mechanism that inserts the cork into the neck of the bottle with precision.
Type of Cap: Corks (typical for wine).
10. Vacuum Capping Head (for Vacuum Packaging)
Description: The vacuum capping head is designed to apply caps on bottles to be vacuum-sealed, as in the case of some vacuum-packaged beverages or foods.
Features:
The cap is applied under vacuum to ensure an airtight seal that preserves the content.
Type of Cap: Vacuum packaging caps (plastic or metal caps).










⇨ OTHER SPARE PARTS ⇦
(For codes, measurements, drawings or other info, send us a request in the "contacts" section)
SUCTION CUPS ➯ GRIPPING TONGS ➯ GASKETS ➯ SEALING RINGS ➯ ROLLERS ➯ PLATES ➯ BUSHINGS ➯ PLASTIC EQUIPMENT ➯ SPRINGS ➯ RUBBER MEMBRANES ➯ IRONING ROLLERS ➯ IRONING BRUSHES ➯ INSERTS ➯ SPECIAL BEARINGS ➯ ETC…















Brands we can provide you:
BUCHER ➯ BONFIGLIOLI ➯ SKF ➯ METAL WORK ➯ STM ➯ OROBICA ➯ CHIARAVALLI ➯ B&R ➯ NORGREN ➯ ROBOPAC ➯ ABB ➯ SITI ➯ OMAC ➯ ROTEN ➯ SEW EURODRIVE ➯CALPEDA ➯ SIEMENS ➯ FRANCESCA POMPE ➯ LOWARA ➯ NSK ➯ AIRON ➯ GAMA VUOTO ➯ REGINA ➯ MGM ➯ SMC ➯ REXROTH BOSCH ➯ TECNOMAXDUE ➯ CORIMA PARMA ➯ DANFOSS ➯ MOTOVARIO ➯ ROSSI ➯ WIKA ➯ BELLOT ➯ MAGRIS ➯ LIVERANI ➯ NSK ➯ IGUS ➯ DELLA TOFFOLA ➯ SYSTEM RES ➯ SYSTEM PLAST ➯ RAVIOLI ➯ POGGI ➯ PRONAL ➯ EBARA ➯ FAG ➯ ISB ➯ CEP ➯ SICK ➯ CSF ➯ MWM ➯ SATI ➯ NERI MOTORI ➯ MT MOTORI ➯ BEA ➯ FLENDER ➯ GEUNDFOS ➯ REXNORD ➯ MITSUBISCHI ➯ HIWIN ➯ PNEUMAX ➯ ELESA ➯ INA ➯ LENZE





















.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.webp)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.webp)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.webp)

.png)
%20(3).png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

We also provide compatible spare parts for the machines
◉ Krones ◉ KHS ◉ Sidel ◉ Bertolaso.
| 901224238 |
| 901224254 |
| 901224412 |
| 901224467 |
| 901225091 |
| 901225339 |
| 901226414 |
| 901226688 |
| 901226829 |
| 901227208 |
| 901227287 |
| 901228065 |
| 901228067 |
| 901228828 |
| 901229623 |
| 901229662 |
| 901229689 |
| 901229911 |
| 901230147 |
| 901230164 |
| 901231516 |
| 901231657 |
| 901231659 |
| 901231794 |
| 901231872 |
| 901232241 |
| 901232309 |
| 901232503 |
| 901233062 |
| 901233162 |
| 901233826 |
| 901233955 |
| 901234107 |
| 901234194 |
| 901234293 |
| 901234318 |
| 901234319 |
| 901234333 |
| 901234335 |
| 901234338 |
| 901235983 |
| 901236273 |
| 901236916 |
| 901237758 |
| 901238218 |
| 901238915 |
| 901239881 |
| 901240046 |
| 901241063 |
| 901241243 |
| 901821176 |
| 7789900555 |
| 560557002 |
| 900018535 |
| 903478516 |
| 624139222 |
| 424946001 |
| 562305121 |
| 5000290273 |
| 902048841 |
| 162202272 |
| 903263263 |
| 901556925 |
| 902730658 |
| 900027505 |
| 901595198 |
| 900214168 |
| 902636738 |
| 7182101246 |
| 689900025 |
| 903053672 |
| 8745522700 |
| 901457128 |
| 902636739 |
| 902636861 |
| 902636862 |
| 689900023 |
| 1786470090 |
| 902636864 |
| 20444119 |
| 900027516 |
| 1099046180 |
| 903174683 |
| 901530083 |
| 1745526470 |
| 162200113 |
| 162200452 |
| 624146142 |
| 681728062 |
| 900027503 |
| 901264064 |
| 902977050 |
| 902289458 |
| 901311321 |
| 902583057 |
| 901643046 |
| 529900332 |
| 1018470350 |
| 901427688 |
| 901700643 |
| 162200124 |
| 900027511 |
| 900027510 |
| 1124503070 |
| 9112810559 |
| 902769843 |
| 900027514 |
| 8125500406 |
| 129900037 |
| 901738080 |
| 900027502 |
| 900060276 |
| 900027501 |
| 900060280 |
| 902581010 |
| 901036127 |
| 902154321 |
| 900027518 |
| 162200117 |
| 900009184 |
| 1224500310 |
| 900027513 |
| 901240046 |
| 162200121 |
| 900027510 |
| 900027517 |
| 901796656 |
| 901796651 |
| 901796741 |
| 901995185 |
0901648499
1786272900
1780331610
0900536474/2786327653
1786330092
0901351410
0901351398
0901600758
0901351410
0901932583
1099047910
902583366
0901555564
0901555564
0901555596
0902816353
0900340586
0901243225
0901243265
0904260357
0904388045
0904388043
0900771117
ù0900754572
0-900-89-855-4
1780331610
0900536474
0902050427
0900947954
0900843069
1788321670,1786331420
0-901-80-657-1
1-786-33-076-0 1786330760
1786327351 1786273830
1-786-41-122-0
0-900-77-111-7
0903791719
0901100690
0900963166, 0900340586, 0900964176, 0900966245(sp), 0902673510, 0900340586, 0902673284, 0904142787, ’0902673284 ,1800205437, 0900697669, 0900697703 ,0900784403 ,0900964053,
0423500009, 0904927507, 0723411242, 0904126649,
0900160135,
0900943949, 0902673285
0901308773
0902998967
0900697703
1786272881
1786272880
0900022938
F-315872.01
Z5034010
0902270336
| 1-224-50-031-0 |
| 1-099-04-641-0 |
| 1-308-51-036-0 |
| 0-162-20-008-7 |
| 0-162-20-050-6 |
| 0-162-20-006-4 |
| 0-169-90-036-2 |
| 0-169-20-005-2 |
| 1-126-51-264-0 |
| 0-126-20-005-9 |
| 1-324-51-115-0 |
| 0-562-31-918-2 |
| 0-162-12-611-9 |
| 0-162-20-134-69 |
| 0-129-90-002-7 |
| 1-326-51-043-0 |
| 8-126-50-0316 |
| 1-326-51-051-0 |
| 1-324-51-066-1 |
| 1-324-51-065-0 |
| 1-324-51-070-0 |
| 0-179-90-183-0 |
| 0-499-90-056-9 |
55381851
55245046
55279125
55446214
55448994
55461774
55461773
55461772
55461771
55461775
55461776
55461777
55480588
55461769
55461770
55526303
55063039
55529891
55532370
55538476
55426590
55413952
55500812
55468982
55539276
55539274
55505086
55394070
55443866
55063043
55525608
55525606
55534371
55070433
55525601
55440433
55383885
55190123
55447125
55450574
55435615
55416979
55027929
55388317
55455887
55031717
55504281
55359561
55440426
55359562
55362443
55525609
55415655
55306666
55310450
55468643
55542304
55321409
55451590
55428625
55383903
55383871
55460761
55438505
55383918
55535022
55396060
55450915
55453951
55398798
55464449
55383872
55383850
55383857
55383856
55429598
55502599
55383868
55383862
55382284
55427612
55540192
55397202
55413142
55507227
55505588
55411019
55462898
55032179
55345346
55323915
55308139
55465918
55465919
55178244
55506557
55309015
55329718
55451652
55514315
55411264
55536139
55413201
55507088
55446481
55418131
55522675
55446127
55517001
55517252
55514062
55518662
55448653
55514068
55508280
55518539
55443366
55521729
55521728
55480708
55522674
55418134
55504792
55443404
55066625
55244663
55066621
55296438
55504338
55448811
55441971
55352766
55446129
55528062
55508279
55522676
55066622
55066644
55529190
55444660
55539273
55539275
55483604
55504790
55386107
55443396
55268643
55352767
55504791
55378968
55443402
55508278
55467357
55354378
55524960
55468635
55526304
55359576
55366301
55527116
55454847
55524103
55509754
55505749
55505748
55505747
55498057
55508135
55508498
55244657
55066652
55443351
55386098
55181296
55437886
55070228
55447258
55063029
55453713
55386110
55443407
55379632
55443405
55443406
55352768
55446128
55524791
55066666
55508137
55524765
55388312
55453215
55437873
55437876
55446131
55413942
55542381
55515216
55453711
55453216
55504786
55504787
55504340
55054827
55388304
55383886
55540727
55459092
55070426
55521730
55517125
55026361
55542947
55054830
55520753
55386105
55443361
55388308
55383883
55359563
55063042
55359580
55545251
55026016
55027129
55506400
55518049
55301444
55518050
55388310
55416158
55472723
55504280
55026301
55506401
55481657
55451972
55387518
55026306
55390235
55545270
55066617
55388309
55545271
55416157
55359612
55181388
55388305
55452548
55435616
55029555
55448583
55530683
55383843
55459470
55185638
55181805
55514856
55544709
55545250
55447588
55066546
55547700
55066523
55529191
55019411
55185635
55019440
55026679
55518534
55437384
55433822
55474164
55495116
55437382
55466217
55505087
55446281
55518535
55474165
55185836
55436362
55032470
55047566
55026548
55528475
55528919
55472749
55028268
55443350
55458561
55457722
55503402
55504800
55504795
55457714
55457713
55513077
55453222
55504796
55026690
55026535
55398041
55070448
55066712
55359538
55388294
55359578
55388319
55463658
55185716
55185717
55066549
55518538
55448812
55019410
55019405
55026748
55296340
55047582
55501397
55446277
55446278
55413934
55026759
55446283
55026609
55047581
55296171
55440422
55440435
55352708
55440424
55018781
55352708
55526837
55278034
55454831
55445276
55458509
55354888
55505341
55433009
55285689
55185194
55454805
55237237
55297177
55026661
55441167
55285658
55413963
55455256
55444466
55181390
55026244
55454841
55454827
55298071
55454804
55322193
55026592
55446284
55028233
55026594
55454803
55415338
55415348
55026476
55464136
55026490
55394096
55026534
55026518
55285667
55285680
55026515
55025984
55514070
55459469
55185408
55491176
55296380
55302635
55446280
55526839
55454806
55440438
55446274
55446275
55285676
55446264
55446265
55026675
55180747
55244659
55463402
55285695
55026967
55021221
55021420
55021232
55026560
55026696
55345319
55429612
55309213
55026561
55026517
55296379
55318990
55285669
55255951
55297656
55462844
55028252
55444222
55322719
55287061
55458098
55455882
55454820
55288998
55514063
55298256
55383434
55437369
55413940
55454825
55440439
55440443
55493806
55376879
55445279
55445278
55306662
55285693
55437845
55446267
55446266
55446273
55446268
55446272
55437846
55446270
55446271
55437848
55296157
55421543
55019318
55316992
55297325
55181382
55029312
55028209
55388303
55388315
55388331
55203065
55029314
55388318
55454145
55545051
55464191
55449124
55449130
55066485
55440421
55454144
55210344
55446279
55181383
55383884
55473189
55383834
55383844
55406776
55190953
55505344
55526300
55505331
55383884
55383915
55383848
55340572
55091464
55518528
55201395
55070220
55344277
55180688
55386072
55070437
55386068
55066765
55529185
55540591
55505329
55472750
55518051
55174243
55388326
55531191
55025304
55495117
55523129
55181806
55488243
55388326
55453134
55066785
55025813
55500652
55454826
55245627
55390239
55415770
55528059
55505325
55496819
55388327
55378113
55490821
55245629
55398108
55181393
55448154
55447257
55436088
55526308
55371736
55461319
55418200
55443400
55434592
55408456
55346967
55500651
55437874
55346954
55025799
55025798
55383914
55383904
55493795
55426596
55245644
55066533
55245310
55243908
55347232
55408462
55026330
55346918
55359629
55507523
55359592
55540194
55359553
55465816
55437875
55528479
55359622
55476120
55026936
55026327
55025983
55026309
55026047
55539579
55523050
55523049
55508599
55523062
55523061
55025996
55508618
55026325
55508620
55505093
55517003
55508617
55026959
55505340
55523281
55523282
55468646
55504339
55540359
55431722
55466475
55466476
55346951
55525890
55517004
55398212
55524982
55468176
55490824
55025834
55524047
55478647
55468178
55476114
55344196
55441768
55517000
55426595
55426594
55500177
55322039
55066739
55468636
55468637
55525899
55525900
55256163
55066714
55505324
55508613
55174225
55504337
55066766
55035067
55025814
55505339
55066789
55066734
55346017
55449135
55386101
55536828
55546892
55276901
55426604
55426606
55359633
55328790
55066706
55066705
55066702
55505349
55026088
55468644
55529184
55025990
55026313
55026310
55362447
55025993
55386108
55386109
55052781
55472272
55028255
55472751
55388314
55027290
55066497
55530687
55530649
55530686
55190471
55383930
55054384
55386070
55025358
55541387
55066725
55410796
55542310
55540196
55525614
55525616
55383931
55198442
55066723
55289609
55491937
55035090
55243690
55280099
55538813
55538812
55531192
55530690
55359542
55525615
55520737
55524491
55524492
55464448
55386057
55388290
55541388
55345320
55066474
55447383
55346785
55385858
55495114
55452062
55455282
55388316
55388321
55388320
55026522
55526305
55386051
55066472
55386058
55516999
55525889
55525901
55345331
55527539
55517002
55440589
55528792
55432174
55523047
55523048
55296603
55525902
55472271
55508133
55488254
55468640
55453412
55418132
55535437
55535438
55468638
55413198
55505096
55448937
55328837
55506397
55506396
55508291
55383830
55386096
55066510
55066502
55523269
55509080
55509036
55509037
55526838
55457499
55454816
55493474
55027561
55468642
55468639
55468641
55451814
55328658
55505746
55446068
55066507
55066509
55549587
55383887
55505745
55478677
55524046
55453710
55463858
55359575
55427821
55526299
55479345
55479347
55508130
55431621
55427629
55427631
55516998
55518536
55516996
55514064
55458435
55427635
55431620
55427637
55427636
55431618
55410354
55452839
55524768
55427638
55516997
55458436
55442820
55181402
55542305
55453413
55027547
55052949
55034916
55067670
55067665
55505094
55435220
55496818
55545269
55545268
55512081
55263773
55185974
55514082
55383649
55514863
55514862
55514864
55509756
55500654
55413869
55505612
55505590
55450567
55505589
55451611
55455572
55386053
55383839
55451822
55451824
55451823
55464447
55493471
55505611
55498058
55530689
55530688
55385859
55386065
55347128
55029639
55385457
55067664
55034907
55383881
55416711
55066738
55512980
55504332
55524767
55523270
55522672
55359570
55522673
55530685
55511522
55421197
55396041
55452957
55452958
55452959
55452956
55421206
55428662
55421199
55421198
55428659
55433792
55476224
55526840
55275274
55455672
55421201
55527552
55383882
55441402
55441403
55441404
55441405
55540190
55540189
55540191
55528478
55472709
| 8AWAA400401 |
| 04250414101 |
| 8DCVL003140 |
| 8AQCA100151 |
| 8AQCA200271 |
| 8AWCC415001 |
| 00000113146 |